[Pipeline Archive] Y-Biologics YBL-006
DATE : 2021.06.21Author : Y-Biologics
VIEWS : 1257
Since May last year, Y-Biologics has been conducting multinational Phase 1 clinical trials to examine the safety and efficacy of YBL-006, a PD-1 antibody, in solid cancer patients. The PD-1 antibody is an immuno-oncology drug that binds to the PD-1 protein, which is the immune checkpoint of T cells, and causes cancer cells to die by preventing them from evading the attacks from the immune system.
Cancer cells express a protein called PD-L1 on their surface and bind to the PD-1 protein on the T cells that are trying to attack them. When an antibody is attached to PD-1 to prevent this, the T cells can attack and kill cancer cells as normal.
MSD’s pembrolizumab (product name: Keytruda), which is dominating the PD-1 antibody market, has been approved by the U.S. FDA for indications for 26 types of cancer and has already become a primary prescription drug for anticancer treatment, with sales reaching USD 14.4 billion last year. Experts predict that it will become a standard anticancer drug in the future, as approval is being granted for combination therapy with various anticancer drugs one after another.
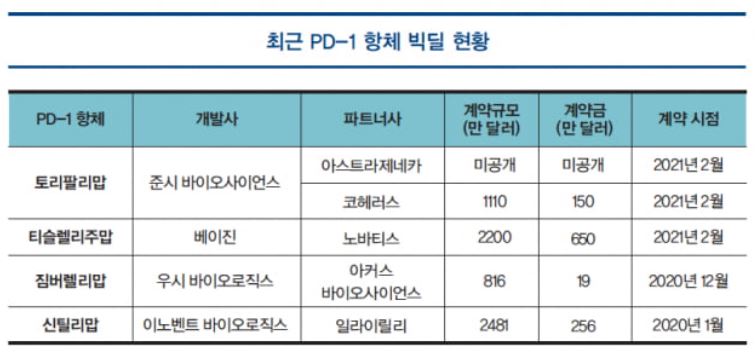
Noticing the success of pembrolizumab, a number of multinational pharmaceutical companies are making an effort to secure PD-1 antibodies by directly developing them or licensing them from developers. This is evidenced by an increase in technology transfers of PD-1 antibodies.
Development Background
One of the core capabilities of Y-Biologics is its ability to discover target antibodies from its own human antibody library, Ymax-ABL, with high efficiency. A PD-1 antibody was selected as a candidate for a new antibody drug by using the library, and it began to be developed in full swing in 2018. A PD-1 antibody is a basic drug for immunotherapy, and it is one of the drugs that are most actively researched to check the possibility of being administered concomitantly with various types of anticancer drugs. This is because it is judged that it is difficult to penetrate the market that is already dominated by multinational pharmaceutical companies, such as MSD and BMS, with a PD-1 antibody without any differentiated characteristics.
If Y-Biologics develops a drug with efficacy equivalent to or higher than that of Keytruda, currently the No. 1 in the market, by applying a new biomarker or combination therapy to the types of cancer with unmet needs, it may become the first domestically developed PD-1 antibody immuno-oncology drug to be marketed, and this will be an important milestone in the development of new anticancer drugs in Korea.
As for the Phase 1 clinical trial of YBL-006, there are plans to confirm the types of cancer to examine in the Phase 2 clinical trial in the future dose expansion study and collect more clinical data.
Antibody Properties
When Y-Biologics screened for an PD-1 antibody from the antibody library, YBL-006 was derived based on the binding affinity to the antigen, PD-1, and the productivity.
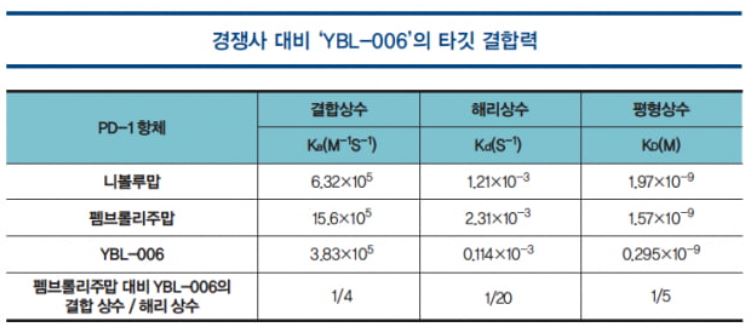
The level of the binding affinity of the PD-1 antibody to the PD-1 protein on the surface of T cells is directly associated with the immune checkpoint inhibitory effect of the antibody and T cell activation. This has a significant impact on the clinical efficacy from the aspect of pharmacodynamics. YBL-006, which was selected from among antibody candidates with strong binding affinity to PD-1, differs substantially from the representative PD-1 antibodies that are currently on the market such as pembrolizumab and nivolumab (product name Opdivo) in terms of antigen-antibody binding properties, and the dissociation rate is significantly low, based on which outstanding efficacy can be expected.
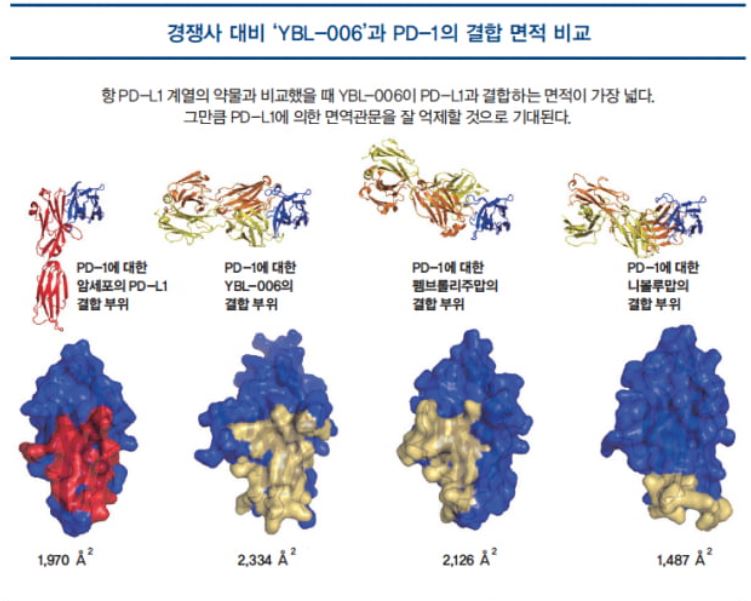
The reason behind these binding properties of YBL-006 can be seen by examining the region where it binds to PD-1 by X-ray spectroscopy. As shown in the figure on the right, the PD-1 antibodies that bind to the PD-1 protein in blue have different binding sites (epitopes or antigenic determinants).YB-006 binds to the area that is most similar to the area where PD-L1 on cancer cells is attached, and the area of the binding site was measured to be 2, 334 A², which is wider than pembrolizumab’s 2,126 A². This signifies that it has an excellent ability to expose cancer cells to the immune system attacks by inhibiting the immune checkpoints that work by binding to PD-1/PD-L1.
Interim Results from Clinical Trials
Y-Biologics has been conducting Phase 1 clinical trials on YBL-006 in Korea, Australia, and Thailand since May last year after completing a non-clinical trial in Canada. A dose escalation test has been completed to determine an appropriate dose, and it has recently begun a dose expansion study to create more clinical cases for specific types of cancer.
In the dose escalation study, eleven patients with solid cancer, such as squamous cell cancer and colorectal cancer, participated, and the dose was increased to 0.5, 2, 5, or 10 mg/kg depending on the weight of the subject. As for the adverse events associated with the drug, one case of Grade 2 cytokine syndrome was reported, aside from fatigue and hypothyroidism, and no dose-based toxicity was observed. As such, it was deemed that there were no safety issues.
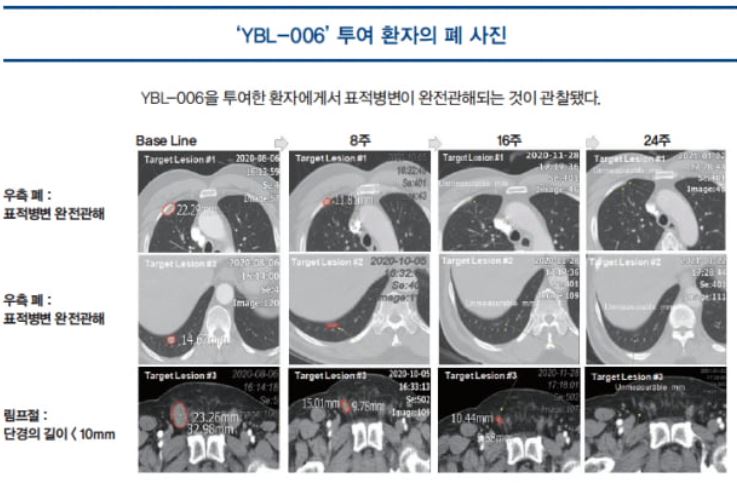
The preliminary efficacy to be reported from the clinical trial was favorable. One subject showed complete remission (CR), with the disappearance of the target lesion, i.e., the tumor. Another subject showed partial remission (PR), with the tumor size reduced to 50%, providing evidence of the clinical efficacy of YBL-006. Two other subjects were classified under stable disease (SD), while the rest of the subjects were judged to have progressive disease (PD). Pharmacokinetic evaluation was also performed in the clinical trial. Based on the results, it was deemed reasonable to apply a single dose such as 200 mg and 300 mg, instead of the initial dose from Phase 1 clinical trial, which was 2 mg/kg at Week 2 or Week 3, like the existing PD-1 antibody drugs.
There are plans to confirm the types of cancer to be targeted using YBL-006 in the Phase 2 clinical trial by conducting a dose expansion test and to collect more clinical cases.
Future Clinical and Licensing Plans
With the goal of developing Korea’s first PD-1 antibody for immunotherapy, Y-Biologics will initiate a Phase 2 clinical trial targeting rare cancers with a small number of patients first. Then, a protocol for applying new biomarkers is also being considered. This is a strategy to have YBL-006 be designated for the fast track process by the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety to facilitate the conditional approval. Under circumstances, obtaining this approval from the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety with multiple PD-1 antibodies already developed will facilitate licensing out
in the conditional permit visibility after being designated as a target of expedited review by the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety. In a situation where a considerable number of PD-1 antibodies have already been developed, it is to more abundantly meet the requirements for license-out through the approval of the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety.
Reporter Choi Jiwon.
